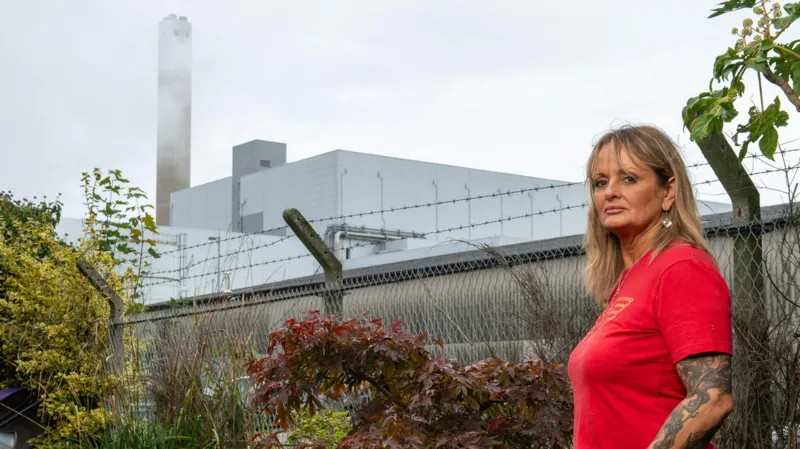
Waste incineration has long been a contentious issue, with concerns ranging from environmental degradation to public health risks. To address these challenges, new and more stringent rules are being proposed to restrict the construction and operation of new waste incinerators. These measures aim to mitigate the environmental impact of waste management, encourage sustainable alternatives, and ensure better oversight of air quality and carbon emissions.
The updated regulations focus on limiting the approval of new facilities by imposing rigorous standards for environmental impact assessments and community consultations. Prospective incinerators will need to demonstrate advanced technologies that significantly reduce harmful emissions, such as carbon dioxide, dioxins, and other toxic pollutants. This move aligns with global commitments to combat climate change and transition towards greener waste management practices.
Additionally, these regulations are set to prioritize public health. Communities near proposed sites often bear the brunt of incineration-related air pollution. To safeguard their well-being, stricter air quality monitoring requirements and enforced emission caps will be mandatory for any operational or proposed facility. The goal is to ensure cleaner air and prevent long-term health issues associated with waste incineration.
Critics of incineration also emphasize its conflict with recycling and waste reduction efforts. New rules may include mandates that waste destined for incinerators first undergo rigorous pre-processing to ensure maximum recyclables are extracted, thus minimizing the incineration of valuable materials.
These tougher measures are part of a broader shift towards promoting a circular economy, which focuses on reducing waste generation and maximizing resource recovery. Governments, environmental advocates, and communities increasingly agree that waste incineration should not hinder progress toward these goals.
The changes may face resistance from stakeholders in the waste management industry due to increased compliance costs and operational challenges. However, proponents argue that the long-term benefits—both environmental and social—far outweigh the short-term inconveniences. By tightening restrictions on new waste incinerators, policymakers hope to drive innovation in waste reduction technologies and reduce the dependency on incineration altogether.
In conclusion, these tougher rules signify a pivotal step toward a more sustainable and health-conscious approach to waste management. With stringent oversight, robust environmental protections, and a focus on waste reduction, the future of waste management is poised to move beyond incineration, embracing more sustainable alternatives.